Chapter 4: Secondary Storage
Learning Objectives
1. Distinguish
between primary and secondary storage.
2. Identify
the important characteristics of secondary storage, including media,
capacity, storage devices, and access speed.
3. Describe
hard-disk platters, tracks, sectors, cylinders, and head crashes.
4. Compare
internal and external hard drives.
5. Compare
performance enhancements including disk caching, RAID, file compression,
and file decompression.
6. Define
optical storage including compact discs, digital versatile discs, and Blu-ray discs.
7. Define
solid-state storage, including solid-state drives, flash memory cards, and USB
drives.
8. Define
cloud storage and cloud storage services.
9. Describe
mass storage, mass storage devices, enterprise storage systems, and storage
area network.
Introduction
· Data storage has expanded from text and numeric files to include digital music files, photographic files, video files, and much more.
· These new types of files require secondary storage devices with much greater capacity.
· In this chapter, you learn about the many types of secondary storage devices including their capabilities and limitations.
· In this chapter, you learn about the many types of secondary storage devices including their capabilities and limitations.
Storage
Primary
storage is:
Volatile storage
Volatile storage
-
Loses content when the computer loses power
Temporary storage
Random Access Memory (RAM)
Temporary storage
Random Access Memory (RAM)
Secondary
storage is:
Non-volatile storage
- Stores programs and data regardless of power
Permanent storage
-
Permanently saves information for future use
Secondary Storage Characteristics
Secondary storage characteristics
Media
Secondary storage characteristics
Media
-
Physical materials that holds data and programs
Capacity
Capacity
-
How much the media can hold
Storage devices
Storage devices
-
Hardware that reads data and programs
Access speed
Access speed
-
Amount of time required to retrieve data from storage
-
Writing is the process of saving information to storage
Reading
is the process of accessing information from storage
Hard Disks
Save files by
altering the magnetic charges of the disk’s surface to
represent 1s
and 0s
·Store and organize files using tracks, sectors, and cylinders
Head Crash
Occurs when read-write head makes contact with the hard
disk’s surface or with particles
on its surface
Types of Hard Disks
Internal
·Located inside the system unit
·Used to store programs and data files
·You should perform routine maintenance and periodically backup all important files
·Located inside the system unit
·Used to store programs and data files
·You should perform routine maintenance and periodically backup all important files
External
·Removable
·Used to complement internal hard disk
Performance
Enhancements
There are 3
ways to enhance performance.
Solid-State Storage
Solid–state
devices (SSDs) have no moving parts
Solid-state
drives
—Faster and more durable than hard
disks
—Access to slash memory or solid state
storage
Flash memory
cards
—Widely used in laptops, smartphones,
GPS navigation systems
USB Drives (or
Flash Drives)
—Connect to USB port
—Capacity of 1 GB to 256 GB
—Portable
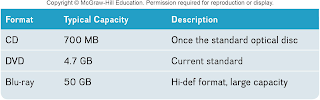
Optical Discs
—Hold over 128 gigabytes (GB) of data
—Use reflected light to represent data
—Lands represent 1s and 0s on the disc
—Pits are bumpy areas on the disc
that, when light is reflected, determine the 1s and 0s
—Use tracks and sectors to organize
and store files but only use a single track unlike the hard drive
Optical Disc Types
Optical Disc Formats
Type
|
Access
|
Description
|
CD-ROM
|
Compact disc – read only mode
|
Cannot be written to or erased
|
CD-R
|
Compact disc – recordable
|
Can be written to
|
CD-RW
|
Compact disc – rewritable
|
Can be written to and erasable
|
Cloud Storage
The Internet
acts as a “cloud” of servers
—Applications provided as a service
rather than a product
—Supplied by servers that provide
cloud storage or online storage
Cloud Storage Services
Benefits / Advantages
•Maintenance
•Hardware upgrades
•File sharing and collaboration
Disadvantages
•Access speed
•File Security
Cloud Storage Service Companies
Making IT Work for You ~ Cloud
Storage
Step1
Dropbox
Step 2
Sharing Dropbox
Mass Storage Devices
—Enterprise storage system
—Safe use of data across an
organizational network
—Devices include:
—File servers
—Networked attached storage (NAS)
—RAID systems
—Organizational cloud storage
Storage Area Network (SAN)
—Architecture to
link remote computer storage devices
—Enterprise
storage systems can be connected to
—Computers to provide local system access
—User’s computer
provides file system, but SAN provides disk space
—House data in remote locations and still allow efficient and secure
access
Careers In IT
—Disaster recovery specialists are responsible for recovering systems
and data after a disaster strokes
—General employer requirements
—Bachelors or
associates degree in computer science or information systems
—Experience in
the field and skills in networking, security and DBA
—Communication and skills and be able to handle high-sress situations
—Annual salary of $70 K to $88 K
A Look to the Future ~ Next
Generation Storage
—At some point,
hard drives will no longer be able to keep up
—Looking at ways
of increasing capacity without increasing size
—Currently hard
drive maxes out at 128 GB per square inch.
—New technologies may advance this to 6.25 TG (6,250 GB) per square
inch.
Open-Ended Questions (Page 1 of 2)
1.Compare primary storage and secondary storage, and discuss
the most important characteristics of secondary storage.
2.Discuss hard disks including density, platters, tracks,
sectors, cylinders, head crashes, internal, external, and performance
enhancements.
3.Discuss solid-state storage
including solid-state drives, flash memory, and USB drives.
4.Discuss optical disks including pits, lands, CDs, DVDs,
Blu-ray, and hi def.
5.Discuss cloud computing and cloud storage.
6.Describe mass storage
devices including enterprise storage systems, file servers, network attached storage, RAID systems, organizational cloud storage, and storage area network
systems.





















No comments:
Post a Comment